Sea Ice Extent
| July 2013 | Sea Ice Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (35 years) | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||||
| Northern Hemisphere | 8.13 | 3.14 | -7.09% | -8.00% | Largest | 31st | 1983 | 10.57 | 4.08 |
| Smallest | 5th | 2012 | 7.67 | 2.96 | |||||
| Southern Hemisphere | 16.81 | 6.49 | +4.60% | +1.00% | Largest | 2nd | 2010 | 16.92 | 6.53 |
| Smallest | 34th | 1986 | 15.32 | 5.92 | |||||
| Globe | 24.94 | 9.63 | +0.48% | -2.18% | Largest | 24th | 1979 | 26.83 | 10.36 |
| Smallest | 12th | 2011 | 23.47 | 9.06 | |||||
Data Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Period of record: 1979–2013 (35 years)
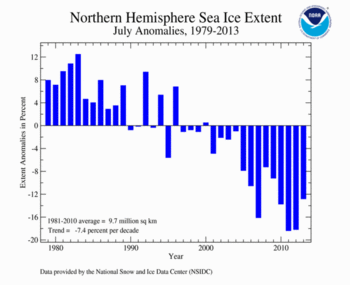
According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), the Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent — which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites — averaged for July 2013 was 8.45 million square km (3.26 million square miles), 12.85 percent below the 1981-2010 average, and the fifth smallest July Arctic sea ice extent on record. The sea ice extent during July 2013 was about 540,000 square kilometers (208,000 square miles) above the record low monthly value in 2011. Over the course of the month, the average sea ice loss was 105,000 square kilometers (41,000 square miles) per day, which was faster than average for the month and second only to July 2007. The Arctic lost ice rapidly during the first half of July and the ice melting slowed towards the end of the month. Over the long-term, the Arctic is losing July sea ice at an average rate of 7.4 percent per decade. Similar to the rest of 2013 to date, below average sea ice was observed on the Atlantic side of the Arctic, with near and slightly above average ice coverage in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas and along the Russian coast.
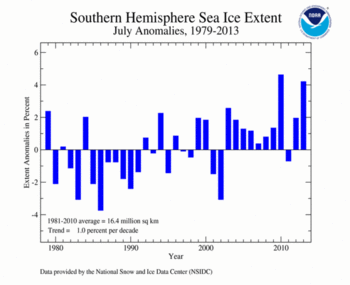
The July 2013 Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent was 17.13 million square km (6.61 million square miles), 4.22 percent above the 1981-2010 average. This marked the second largest July Antarctic sea ice extent on record, behind the record large July extent of 17.20 million square km (6.64 million square miles), set in 2010. July Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent is increasing at an average rate of 1.0 percent per decade, with substantial interannual variability.
When combining the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere sea ice extents, the globally-averaged sea ice extent during July was 25.58 million square km (9.87 million square miles). This was 570,000 square km (220,000 square miles), or 2.2 percent, below the 1981-2010 average of 26.13 million square km (10.09 million square miles) and the 12th smallest global July sea ice extent since records began in 1979.
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information