Updated: 11 April 2013
Overview
Wildfire activity flared across the southern U.S. in early March with large fires erupting in Oklahoma, Texas, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida. Outbreaks increased across the Southeast and stretched into the Ohio Valley later in the month. Colorado experienced its first major wildfire of the season at mid-month. Numerous fires in the Lower Mississippi Valley resulted by the fourth week of March as dryness built in parts of Arkansas and Missouri and along the Gulf Coast. Isolated wildfires occurred in southern Arizona and Puerto Rico in late March.
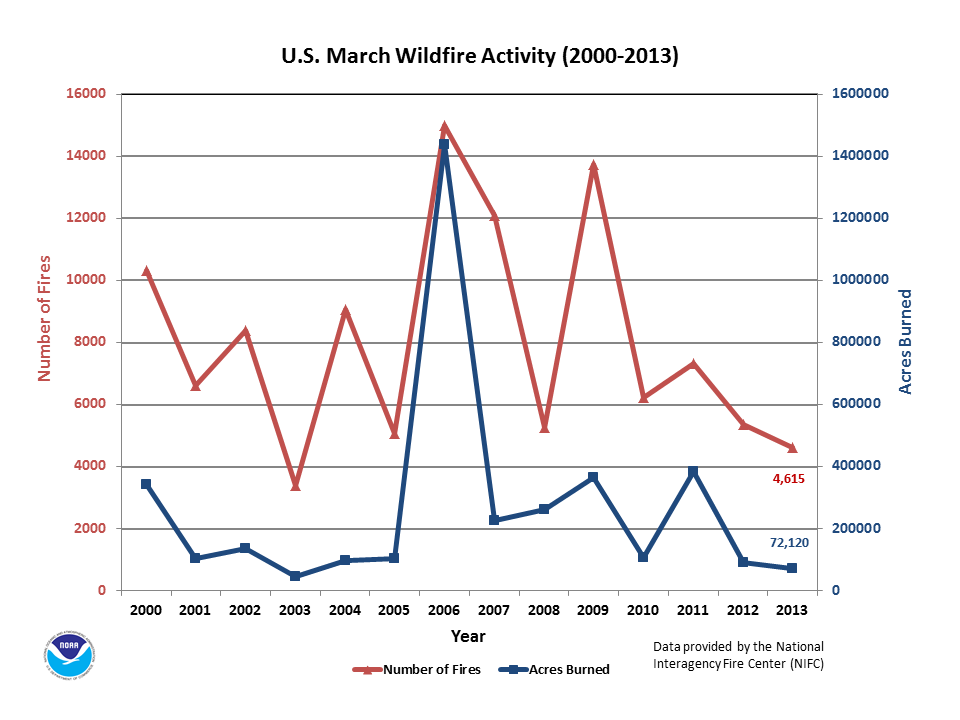
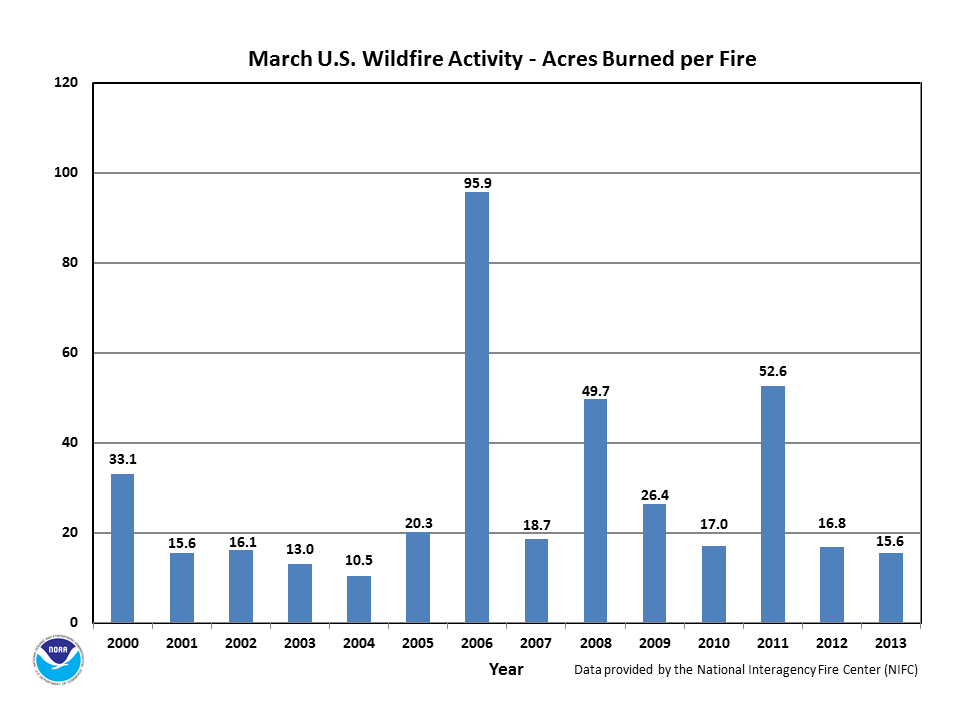
March wildfires accounted for two-thirds of the country's year-to-date number of fires and 77 percent of the acres burned since January. More than one-quarter of the acres burned in March resulted from Florida's Huckabee wildfire during the final days of the month. Yet, the year-to-date number of fires (6,919 fires) as well as the total acres burned (93,125 acres) were both the least on record since 2000 for any January through March period.
According to the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC) :
For more wildfire statistics visit U.S. Wildfires.
NOTE: March totals were increased by 19,354 acres for the Huckabee Fire (from 73,771 acres to 93,125), which occurred after the NIFC daily statistics were released the morning of March 29, 2013. The number of fires was increased by 1 (from 6,918 fires to 6,919).
Discussion
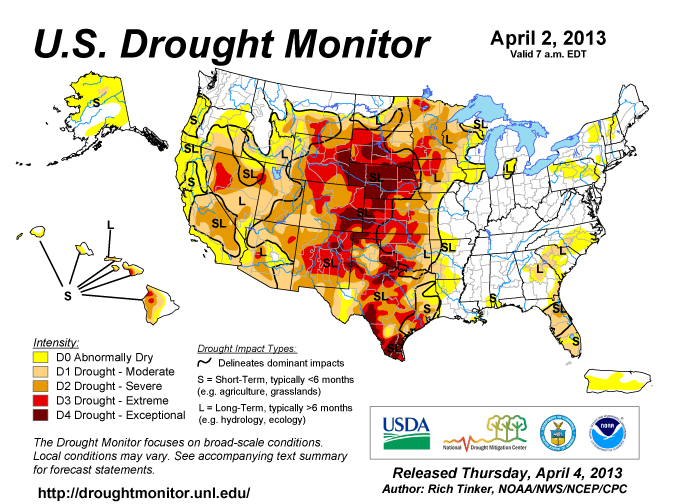
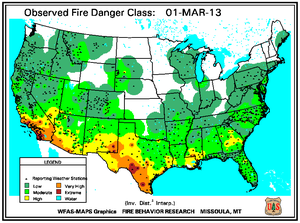
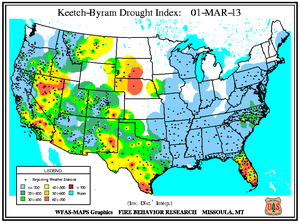
Despite several storm passages throughout March, most areas of the U.S. received near- to below- normal precipitation. Above-normal rainfall ended the severe drought in Georgia persisting since September 2010. Rainfall greatly reduced drought in Missouri and across Iowa. Drought conditions improved in parts of the Southeast (South Carolina and Alabama) and the Central Plains (northwestern Kansas, the Oklahoma and Texas panhandles, eastern Colorado, and south-central South Dakota). Dryness eased in central Arizona and central Virginia. Expansions of drought occurred in central and southern Florida and southern Texas, which coincided with wildfire incidents. Dryness increased in southeastern North Carolina, extreme southern Alabama, and around the border between Arkansas and Louisiana. These locations also closely coincided with large wildfires. Exceptional drought remained entrenched over most of Nebraska and the southern tip of Texas, with some intensification in northwestern South Dakota.
Significant Events
Please note, this is a list of select fires that occurred during March. More comprehensive fire information can be found through Inciweb.
Colorado
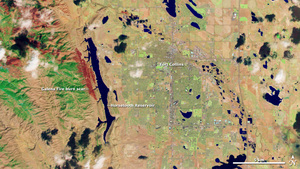
Windy, dry conditions and a lack of snowpack along Colorado's Front Range foothills facilitated an early start for the state's 2013 wildfire season. The Galena wildfire sparked in the Soldier Canyon west of the Horsetooth Reservoir near Fort Collins on March 15th and spread quickly through nearly 1,350 acres in steep, rugged terrain around the Lory State Park. More than 50 homes were threatened by the flames and several hundred Larimer County residents received notification to evacuate. As many as 130 firefighters battled the blaze and two injuries were sustained. No damages to structures were reported. Last year another Colorado wildfire, the Lower North Fork fire, occurred in late March to the southwest of Denver, where it blazed over 4,100 acres in Jefferson County and resulted in four fatalities. Moreover, the Fort Collins area suffered the second largest fire in the state's history in June 2012, when the High Park fire burned nearly 87,300 acres, destroyed 259 homes, and claimed one life. The Galena wildfire's timing posed added risk to the situation, given the fire occurred before the seasonal hiring of the tactical support provided through federal resources was completed. According to media reports, a lag in availability of firefighting aircraft was experienced. High winds hampered the efforts of the aerial support which responded to the incident. During March, the Colorado State Forest Service released an on-line mapping tool, the Colorado Wildfire Risk Assessment Portal, for users to access information relating to likelihood of an acre burning, potential fire intensity, historical fire occurrence, and values at risk from wildfire.
NASA's new Operational Land Imager (OMI) sensor on-board the Landsat Data Continuity Mission satellite produced the image of the Fort Collins area in wavelengths not usually visible to the human eye. The imagery uses a blend of shortwave infrared, near-infrared, and green wavelengths, combining visible and infrared light to reveal features of the landscape not otherwise visible. Plants are shown in green, city areas in purple, snow in pale blue, and bare earth is tan-pink. The Galena burn scar is shown in dark red.
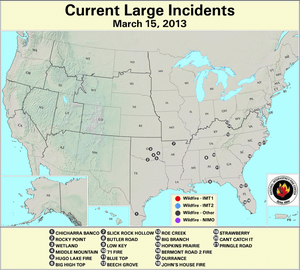
South Carolina
Dryness in the Southeast combined with warm temperatures, low relative humidity, and gusty winds to elevate fire danger levels during March. In South Carolina, 26 residential buildings were destroyed by wildfire in the Carolina Forest community near Myrtle Beach on March 16th. Flames engulfed about 108 condominium units at the Windsor Green complex, where at least five persons received medical assistance, according to media reports. Red Cross volunteers from the Midlands responded with emergency shelter, food, water, and clothing. Meanwhile, at least 64 fires burned across the state. Tragically, a firefighter died while responding to a wildfire near Ridgeville on March 10th. The fire was located in the Francis Beidler Forest, a swamp ecosystem containing deep bald cypress and tupelo gum flats.
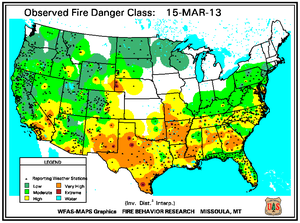
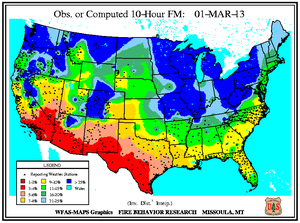
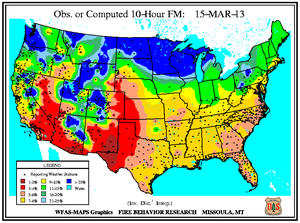
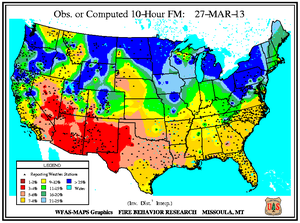
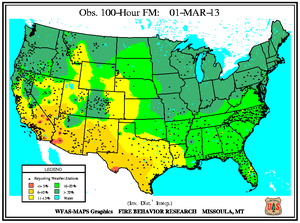
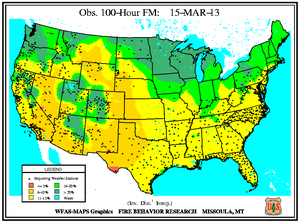
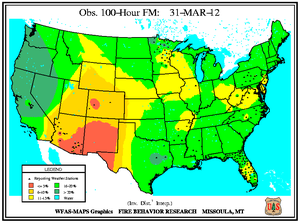
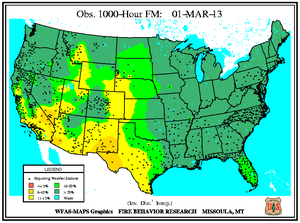
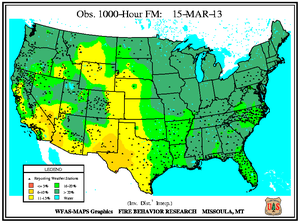
Monthly Wildfire Conditions
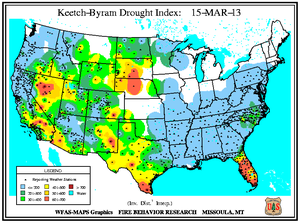
Wildfire information and environmental conditions are provided by the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC) and the U.S. Forest Service (USFS) Wildland Fire Assessment System (WFAS).
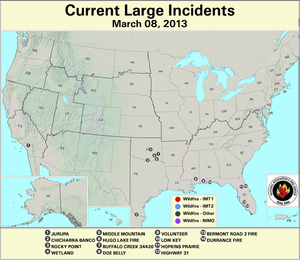
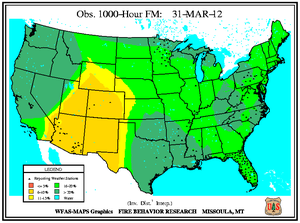
Southeastern Oklahoma experienced an outbreak of several large wildfires during the first weeks of March as 10-hour fuel moistures decreased from ten percent to eight percent. Though drought has reduced the overall grassy fuels available for wildfires, the dead grasses and other dead fuels (leaves, wood on the ground) served as the state's primary fuels. Recent precipitation events since early February permitted larger diameter fuels (1 inch or more) to retain moisture at the 100-hour (above 10 percent) and 1000-hour intervals (above 15 percent). The Rocky Point wildfire burned 3,000 acres of timber and grass to the southeast of Marietta, while other timber and grass fires including the Middle Mountain (near Clayton), Hugo Lake (near Cromwell), and Buffalo Creek (near Talihina) consumed between 300 and 600 acres each. Almost ten million acres (approximately 25 percent) of the state is forested and the forest industry contributes more than $2 billion U.S. dollars to Oklahoma's annual economy.
In east-central Texas, the Iron Bridge Park wildfire burned over 500 acres to the south of Mother Neff State Park between March 3rd and 10th, according to media reports. After igniting from a campfire in Bell County, the wind-fanned flames spread to Coryell County. The fire prompted evacuation of nine families as well as a local campground and threatened at least six homes before being fully extinguished when rain fell over the area. Meanwhile in the state's west, resources management officials leveraged a respite in fire weather danger conditions to relocate pronghorn antelope from the Texas Panhandle to the Trans-Pecos region during early March. Drought and wildfire in Far West Texas rangelands resulted in an abundance of weeds and other invader plants upon which antelope graze. The 130 animals were transported nearly 500 miles from Dalhart to Marathon for release into 70,000 acres of the Chihuahuan Desert.
In Florida's Panhandle, the Low Key wildfire scorched over 5,000 acres of southern rough (flammable evergreen shrubs) to the northeast of Navarre between March 5th and 8th. In central Florida and the Peninsula's southern tip, wildfires coincided closely with locations where the Keetch-Byram Drought Index (KBDI) exceeded 600 units. Along the state's northeast coast where 10-hour fuel moistures ranged from seven to eight percent, the Durrance wildfire burned over 1,100 acres in Volusia County. About 300 homes near Ormond Beach were evacuated and Interstate 95 was temporary closed on March 2nd. The Hopkins Prairie wildfire in central Florida's Ocala National Forest, which blazed over 1,800 acres of timber between March 2nd and 9th, threatened 15 homes at one point, according to media accounts.
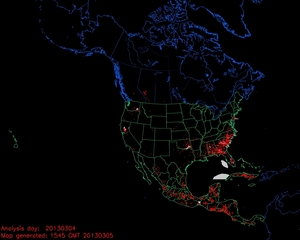
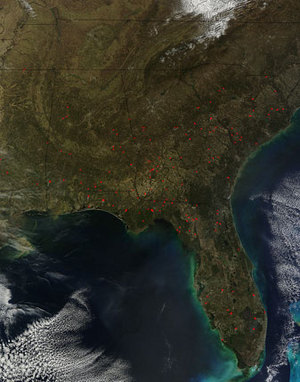
Hazard Mapping System Fire and Smoke Analysis
on 4 March 2013
Source: NOAA Office of Satellite and Product Operations
On NOAA's Hazard Mapping System (HMS) map products, the red dots correspond to hot spots and the grey areas represent smoke plumes from possible fire locations (including prescribed fires) detected over North America by satellite observations. Over 600 acres in southwestern Virginia burned as at least ten wildfires sparked in early March. The largest of those fires, the Beech Grove wildfire consumed over 400 acres of grass and woodland in Scott County on March 10th, according to media reports. Firefighters battled the intense blaze in steep terrain using bulldozers to reduce the spread of flames, which at one point threatened at least 18 structures. Earlier in the month, a Virginia firefighter died while assisting at the scene of a wildfire located in the North Carolina section of the Mackay Island National Wildlife Refuge on March 3rd.
Multiple fires burned along the southeastern coast of North Carolina in early March. The Cant Catch It wildfire charred over 450 acres to the southwest of Jacksonville in Onslow County on March 10th. Flames destroyed an outbuilding and 20 homes were evacuated overnight, according to media reports. Another fire blazed about 400 acres in the Croatan National Forest, which lies to the east of Jacksonville.
A wildfire in the Appalachian Mountains of eastern Tennessee, which swept through 160 acres on March 17th, consumed 65 cabins at the Black Bear Ridge resort near Pigeon Forge. The Tennessee Army National Guard provided aerial support to firefighters by using helicopters to drop buckets of water from the Douglas Lake on the blaze. About 150 people were evacuated due to the fire. In a separate incident a few miles away, a brush fire flared on the Dollywood theme park property, but was extinguished before any damage to the park resulted, according to media reports.
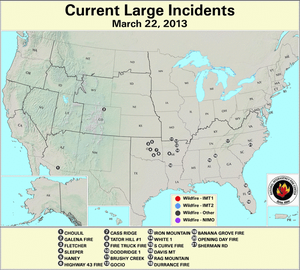
In southwestern Missouri, the Brushy Creek wildfire consumed 350 acres on March 16th near the city of Ava. Meanwhile, large wildfires flared across Arkansas during the latter part of March. Multiple fires sparked on March 16th, which ranged between 120 and 150 acres, primarily fueled by small branches, leaves, and pine needles dislodged during December ice storms. The Gocio wildfire burned 120 acres to the west of Byron on March 20th. Earlier in the month, the Slick Rock Hollow wildfire consumed over 1,200 acres to the north of Cozahome after igniting on March 8th.
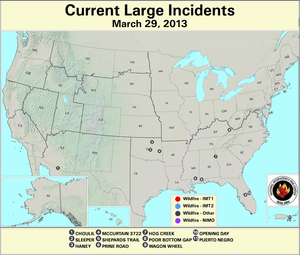
In southwestern Arizona, the Choulil wildfire blazed over 410 acres of grasses to the northeast of San Miguel between March 20th and 22nd. In the southeastern part of the state, the Clay fire burned over 450 acres near Fort Thomas after sparking on March 29th. Southern portions of Arizona and New Mexico experienced critically low fuel moistures of 5 percent and below at both the 10-hour and 100-hour intervals by month's end.

Huckabee fire burned in Florida's
cypress swamp in late March 2013
Source: National Park Service
Photo Courtesy of Cass Palmer
Areas along the Gulf Coast experienced wildfires in late March. The Shepards Trail fire in the De Soto National Forest consumed nearly 4,000 acres of timber and grass between March 25th and 31st near Brooklyn, Mississippi. In Florida the Huckabee wildfire swept through close to 20,000 acres of the Big Cypress National Preserve's tall grass and dry cypress strand since igniting on March 29th to the east of Naples. The fire's dense smoke forced a closure of Interstate 75 and State Road 29 in Collier County from March 30th to April 1st. A section of Interstate 75 in Hillsborough County was closed several hours on March 30th due to poor visibility caused by another fire's smoke. The second wildfire, which burned around 50 acres near Tampa, destroyed a mobile home and several vehicles, according to media accounts.
Severe precipitation deficits on the eastside of Puerto Rico's Vieques island facilitated the Puerto Negro wildfire, which consumed 1,500 acres between March 26th and 31st. Earlier, the main island's La Roceta wildfire near Lajas burned over 135 acres on March 2nd.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information